Telemedicine -Greece
Perfilado de sección
-
General

Rotterdam University of Applied Sciences and the University of Utrecht, with the cooperation of the Social Cooperative of Cyclades as the receiving Organisation, organise a Minor Project for Telemedicine in Greece.
The traineeship is aimed at investigating and finding ways to improve the telemedicine system in Greece.
To do so, we applied the method of Design Thinking. This method offers a range of tools to help find a solution to complex problems.
The activities consist of visiting health care organisations in Greece, interviewing people who are involved with telemedicine, applying tools to better understand the problem, finding ideas and experimenting with solutions.
Telemedicine is considered the most important technology, as it enables effective patient treatment at a low cost. Today, it may seem to be a novel approach, but very soon, telemedicine software will be commonly used by healthcare professionals.
Four students from the Netherlands have developed this E-learning in collaboration with Miltos Sakellariou, Chairman of the board at Altera Vita.
E-learning is aimed at students in medical universities, to inform and enthusiasm them about telemedicine.

-

Welcome and thank you for your attention to this e-learning. As a consequence of technological development in combination with healthcare, telemedicine emerged. Telemedicine is becoming more and more important in the future of healthcare
.

Why this E-learning?
Greece has a peculiar geography that creates an increased need for medical staff. Telemedicine is an important means to solve this problem. Field research showed that students in Heraklion, Crete, are not yet familiar with the term ‘telemedicine’. This e-learning is intended to change this.
What is telemedicine?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has referred telemedicine as "healing from a distance." The telemedicine software is used to provide clinical services to the patients from any remote location.
Telemedicine would be considered as the most important technology as it makes it possible to treat patients effectively at a low cost. Today, it may seem to be a novel approach, but very soon, telemedicine software would be commonly used by healthcare professionals.
Nowadays in Greece, Vodafone has implemented a telemedicine program in 2006. It is located in 100 remote locations on the mainland and on islands in Greece. The Vodafone network is used to send examination or test results to specialists in another location. Also, it has the ability to create an electronic medical record. Vodafone also provides telemedicine training for health care professionals (Vodafone, 2018).
The e-learning consists of six sections. It is intended that one section per week be completed. The following topics are covered:
Lesson 1: Introduction
Lesson 2: Benefits and drawbacks of telemedicine
Lesson 3: Telemedicine history and current situation in Greece
Lesson 4: Types of telemedicine
Lesson 5: Telemedicine devices
Lesson 6: The future of telemedicine
Each week will offer a range of text information, videos and scientific articles. At the end of each section, there are ‘check yourself’ questions to check if you understood the information correctly.
This video gives you an impression of how telemedicine is used
We hope that this e-learning has added value to your medical career.
If you have any questions or feedback you can contact Laura van Weelde; lauravanweelde@gmail.com. Thank you for participating
-

The idea of talking to a doctor or a health care provider from a distance did not arise in the last century or the one before it, this idea has a long history and a lot of experience story that has designed different ideas and encouraged different people to develop a tool that can help to treat as many patients as possible.
In this first lesson, a small part of the history of telemedicine is introduced and we are also gone take a look at how Greece implemented telemedicine for the first time until now.

In 1860 the Telegraph was used for the first time in the war. William S. Morris and Albert James Mayer have developed a system to use the Telegraph to request medical supplies for the frontlines, specify delivery points and coordinate patient transport.
In 1874 in Australia was the first documented use of Telegraph for medical purposes. That happened when the Barrow Creek telegraph station was attacked. A police officer was seriously injured, a surviving policeman asked for help via the Telegraph. Dr. Charles Goose how was informed, gave instructions on how to treat the injured men through the Telegraph until an ambulance arrives.

The next case where Telegraph was used was in west Australia where a twenty-nine-year-old farmer fell off his horse, his friend took him to the nearest town hall (75 km), but there was no hospital or doctor in that city. Via the Telegraph they could reach a doctor who made a diagnosis. However, because the man had to undergo surgery immediately and due to the lack of medical devices, the man died shortly thereafter. The next day the story was on the front pages of all newspapers.
This story inspired John Flynn to develop the world's first Medical Aviation Service in Australia. This organization was organized in 1928 under the name Aerial medical service (AMS), this organization makes it possible to reach patients quickly in remote places in case of an emergency.
The founder of AMS has indicated that radio can reduce the work of AMS by 75%. However, the electricity was not optimal around this time. But Alfred Hermann invented the Pedal radio (a dynamo generator with a pedal drive that was used for electricity supply) at the beginning Morse codes were used and after 1930 was the sound massages were used.

In 1940, all AMS locations were provided with all the devices needed for telemedicine. With the further development of technology and the invention of television, the telemedicine system could further develop. In 1947, the TV was used for the first time to broadcast surgery to doctors in training. In 1951 the telemedicine system was further developed into a colored TV system. The system was also used for video conferencing this year. The cable television system connected in 1968 the university of Nebraska Medical Center and three hospitals for veterans (in Omaha, Lincoln, and Grand Island). Besides, the telemedicine system was further developed this year with devices such as the electrocardiograph, stethoscope, microscopy, voice, and other capabilities. (Vladzymyrskyy, Jordanova, & Lievens, 2016)
The twentieth century had an important role in the development of telemedicine, but the twenty-one century has also made enormous progress for telemedicine, Such as using a mobile phone to take medical care to a remote location, introducing the High-tech camera that makes teledermatology possible through clear photos of the skin and enabling teleradiology through radiographic images and making it possible to forward patient information easily and quickly to other healthcare providers far away.
Telemedicine and Greece
The Greek telemedicine program was started in 1989. the first impetus was between the Internal Medicine Department of the Sismanogleion Hospital and the first-line centers of Spata, the island of Paros, the Hospital of Karpenision and the Primary Care Department of West Fragista.
In 1990 the Greek health minister financed the installation of three terminals in primary health care, for which an agreement was signed with the Greek telecommunications provider (OTE). Two terminals were placed in Sismanogleion hospital one in the Medical Physics Laboratory of the National Kapodistrian University of Athens.

Isolated islands such as Limnos, Ikaria, Faros, Skopelos, Santorini, Astypalaia, Fourni and Kastelorizo were supported in 1992 with the telemedicine service. In April 1992 the connection of primary health care was complete. Afterward, 2000 cases were served.
Pneumatological: 27%
Cardiological: 17%
Orthopaedics: 21%
Ourology: 5%
Surgery: 2%
Supporting and Diet: 12%
The same year the regular teleconsultation service for medical diagnosis was established via the Sismanogleion Hospital Telemedicine Unit on different islands. The last development of telemedicine in Greece was in 1999 the country towards the design of an integrated national telemedicine action plan. This plan was implemented of the study in 1998 that was funded by the Greek ministry of health.
-
The video above shows the reason why telemedicine is important. Of course, like any technology, telemedicine does have its own benefits and drawbacks. Telemedicine has been around for a while now and a lot of problems with it have been fixed.
- Telemedicine supports general practitioners and rural practitioners. The GP's in rural area's can ask for support from specialists to help their patients better.
- The Vodafone telemedicine program promotes preventative medicine and therefore helps prevent diseases through their early diagnosis.
- It covers patients with chronic diseases, as it enables them to systematically monitor their health status at their place of residence, removing geographical or other restrictions.
- Telemedicine has the immediacy of the help that can be provided.
- It prevents the abandonation of remoted places.
- Telemedicine reduces health care costs.
- It even reduces the emission of atmospheric pollutants.
- A drawback for telemedicine is that the medical consultant loses a lot of the information he or she would get from direct contact with the patient, and it may not always be possible to help immediately.
A study of the benefits of telehealth divided the patients into two groups, one where the patients visit a geriatric service and the other is Telegeriatric where patients have a videoconference with a general practitioner. In conclusion, the Telegeriatric reduced the wait times, had a geographically broader reach, and was able to reach more remoted areas compared with the geriatric service. For the results of the article click “Improving geriatric care and reducing hospitalizations in regional and remote areas: The benefits of telehealth”.
Telemedicine significantly reduces the health care cost by saving money for the health care provider, the patients, and insurance. It also reduces unnecessary non-urgent ER visits and eliminates transportation expenses for regular checkups.
Another study shows that between January 2018 and June 2019 in total 9034 face-to-face visits were avoided in 2 hospitals. For an average journey of 25 minutes to the hospital and back a total of 11,754 L of petrol were saved whom would have cost 15,664 euros. Total reduction in pollutants is 29.384 tonnes of carbon dioxide and 36.61 kg of carbon monoxide. Therefore, Telemedicine reduces the environmental impact of atmospheric pollutants emitted by vehicles by reducing the number of journeys made for face-to-face visits to see a specialist. For the results of the article click “Impact of a Telemedicine Program on the Reduction in the Emission of Atmospheric Pollutants and Journeys by Road”
To sum all these benefits up, you can watch this American video about how telemedicine can improve care
- Telemedicine supports general practitioners and rural practitioners. The GP's in rural area's can ask for support from specialists to help their patients better.
-

When a person thinks of telemedicine the first thought that will pop in their mind is a teleconference with a doctor about acute health situations. So, there is no doubt that telemedicine is a great help in acute cases but is actually more than that. Telemedicine can help in different ways. The types of telemedicine that we are going to discuss:
- Medications management
- Triage
- Prevention
- Real-time/ live telemedicine
- Remote patient monitoring:
- Store-and-forward
- Specialist consulting
Medication management
Patients with chronic diseases usually receive medication for a long time. when patients start taking new medication, it usually takes a while for the caregivers to find out whether the medication is effective and whether the patients have the correct dosage. the patients and caregivers have to address the side effect to determine if it is the right medication for the patients. The use of telemedicine by video and audio can ensure that the med checks can happen as much as necessary without placing a burden on both parties.
Triage
Patients with chronic illness can develop new symptoms. It is often difficult for the doctor to determine by telephone whether it is an underline of a disease or a new disease that needs to be treated. Telemedicine can be used to quickly assess the new symptoms via video conversation. This way patients can be reassured or start a new treatment if the symptoms indicate a new disease.
Prevention
Some patients can be a risk group for a certain chronic illness. To prevent them from developing chronic disease, patients usually need to change their lifestyle to ensure that patients are successful they need monitoring and support. It is often very difficult to book such an appointment, which is why telemedicine can play an effective role.
Real-time/live Telemedicine
real-time/live telemedicine makes it for patients and doctors easy to have a visit anytime and anywhere they want. it is a two-way communication that let patient and health care providers communicate in real-time.
Remote patient monitoring
This type of telemedicine allows health care providers to monitor patients from far. Using RPM (remote patient monitoring) can cut down on the time that the patient spends in the hospital. Especially for patients with chronic conditions is very effective to spend time at home instead of in the hospital. Nowadays technology is so evolved that patients do not monitor themselves, but rather vital health data will be shared with the doctor and other health care providers automatically. Thanks to this technology the doctor can provide much better care and take action immediately by any signs of trouble.
Store-and-forward
Store and forward ensures that patient data and medication data are accessible across long distances. a caregiver can collect, upload and leave the required information for the doctor to assess it later. The advantage of this type of telemedicine is that it is not necessary to be assessed immediately by the receiving doctor. another big advantage is that there is no appointment required, therefore, this type of telemedicine is often used to assess minor medical issues. a lot of specialism uses this type of telemedicine to offer better care. Therefore, several systems ensure that all this information is integrated into a single record for each patient.
Specialist consulting
Specialist consulting is deployed to improve the collaboration between the medical team and to offer patients the best care and save them the long journey. through safe video conferencing with or without the patients in the communication room, the patient information can be quickly and completely shared with a specialist. this type of telemedicine has a big advantage in remote places, where the hospitals are far away. This type of telemedicine. In some hospitals and clinics, special examination cameras are available so that the specialized can get a better picture of the condition of the patient
The video below shows how some telemedicine devices are used -

Most people have access to basic telecommunications technology, like telephones, the internet, and computers. But many telemedicine solutions require more equipment than just those basics. Here’s a review of the types of telemedicine equipment a healthcare provider may need.
Telemedicine cartsThis equipment gives providers a mobile frame and storage to carry the cameras, computers monitors, keyboards, computers, and mobile medical devices. The carts look similar to standing work desks, with computer monitors attached at the top and wheels at the bottom for easy moving. These carts are usually used at hospitals or other large health care systems.
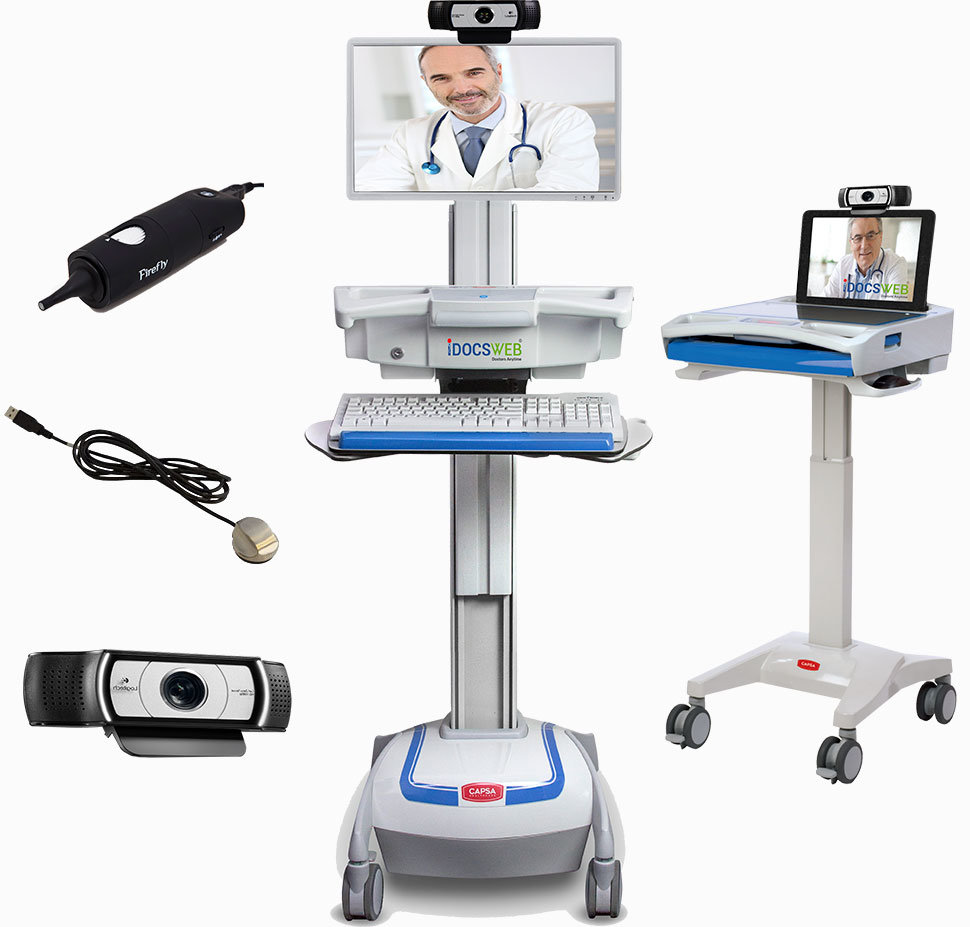
Telemedicine kiosks
The telemedicine kiosk looks like a photobooth and is usually stocked with all the equipment and commonly used mobile medical devices that are needed for a telemedicine visit.
Digital camera
A webcam is needed in order to have a video conference. There are also high-end, high-resolution digital cameras for crystal-clear video capture. The high-tech camera allows the healthcare professional to take detailed medical images and share them with a specialist at another location. It is usually used for store-and-forward telemedicine solutions between two healthcare providers.
Telemedicine kit
Healthcare providers who are routinely providing frontline care in remoted areas need a portable telemedicine kit. The kits often look like sturdy briefcases or large medical kits. Inside the kits are a small computer with an integrated screen, a camera, and simple medical devices.
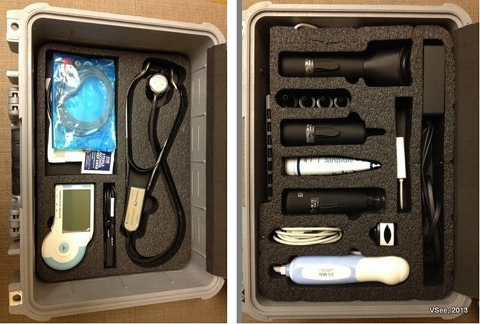
Telemedicine software
A software system needs to be installed on the medical practice’s computers. These software solutions may require additional equipment like data storage hardware or servers
Patient medical record
Vidavo is the system that is used in Greece to process all the patient's medical data. There are also applications of this system. This makes work easier because doctors no longer need to carry a laptop or computer around, instead, all they need is a tablet or a phone.
When the patients visit the doctor, the doctors start to fill in the personal data of the patients in the application. Next, the medical history of the patients is fill in. After that, the reason for the visit will be entered. Then the doctor will test the necessary body functions that happen with a certain medical device. Think about a Blood pressure meter, Spirometer, Electrocardiography (ECG), Oxygen saturation measurement or blood sugar meter, these medical devices are all connected to the application through Bluetooth, which results in equal results and then the doctor can send the visit results to a specialist if necessary.
-
 There’s a lot to be optimistic about in the future of telemedicine. With rapid advances in technology, it’s likely that telemedicine will only become easier and more widely accepted in the coming years. The rate that technology is progressing, telemedicine will of course need to overcome administrative barriers, such as restrictions placed on telemedicine practice by state legislation, state-specific licensing requirements by medical boards, and the reimbursement policies that affect whether doctors are reimbursed by payers and patients are not out-of-pocket. But with the projection that telemedicine will be a $36.3 billion industry by 2020, over 50 telehealth-related bills in the 113th Congress, and 75% of surveyed patients reporting interest in telemedicine, telemedicine’s future is bright and demand is likely to overcome these barriers (E-visit, 2018)
There’s a lot to be optimistic about in the future of telemedicine. With rapid advances in technology, it’s likely that telemedicine will only become easier and more widely accepted in the coming years. The rate that technology is progressing, telemedicine will of course need to overcome administrative barriers, such as restrictions placed on telemedicine practice by state legislation, state-specific licensing requirements by medical boards, and the reimbursement policies that affect whether doctors are reimbursed by payers and patients are not out-of-pocket. But with the projection that telemedicine will be a $36.3 billion industry by 2020, over 50 telehealth-related bills in the 113th Congress, and 75% of surveyed patients reporting interest in telemedicine, telemedicine’s future is bright and demand is likely to overcome these barriers (E-visit, 2018)In the future, telemedicine could be filled in by communication apps for your mobile phone, like WhatsApp. ‘’ Clinicians have independently discovered that they can use their favourite instant messaging app to send text messages to colleagues to seek or give clinical advice, supplemented with images, video, or audio recordings made using their phone. This is counter to current conviction about how to implement scalable and sustainable telemedicine services. No needs or eHealth readiness assessment is undertaken, no business or change management plan formulated, no new software has to be installed, no training is required, and typically there is no budget.’’ (Mars, M., Morris, C., & Scott, R. E., 2019). Literature found in this article showed that clinicians use communication apps because of their simplicity, timeliness and cost-effectiveness. But it also shows that there are no general guidelines available for the use of communication apps in healthcare.
In another article written in 2018 Nikolic, A., Wickramasinghe, N., Claydon-Platt, D., Balakrishnan, V., & Smart, P. are describing positive points about using communication apps in healthcare. Doctors who were participating in this trial were positive, but the privacy policy can not be insured by using these communication apps.
The use of communication apps could be very useful in the future for telemedicine. But there is more research needed to develop guidelines and solutions, due to the privacy issues.
In this E-Learning, a lot is written about the use of telemedicine for doctors, but for other professions, telemedicine can be helpful as well. Physiotherapy, speech and language therapy, dietician, and occupational therapist can use telemedicine as well.
Telesurgery
In 2001, the world’s first telesurgery was conducted by a surgical team in New York, USA. Since then, using telesurgery technology is at a halt. ‘further optimization of visual display, latency time, and haptic feedback technology, design and publication of further randomized controlled trials, and minimization of the factors that limit its clinical translation, telesurgery’s widespread implementation in clinical settings will become highly feasible’ (Choi, Oskouian & Tubbs, 2018).
This video gives you an impression of telesurgery with the Sina robot
There is already research going on about the use of 5G cellular technology. This technology is likely to improve remote assistance in telemedicine and real-time. If you are interested, the following article is about a pilot project that will use 5G cellular technology to enable remote assistance for surgical procedures in real-time. You can find it by clicking on this link:
https://healthmanagement.org/c/healthmanagement/issuearticle/5g-opens-the-future-of-telesurgery
-

Caregiving from distance can be used for other specialties, besides doctors. Telepsychiatry is a well-known appearance in the Greek health care system.

Depression is a well-known appearance in health care. Telemedicine can be useful for a client who experiences some kind of depression. Research about sending text messages to the psychiatrist is done in 2019. It shows that telemedicine can be useful when using real-time, but there is more research needed for sending text messages to the psychiatrist. The research can be found below ‘’ Effectiveness of text messaging interventions for the management of depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis’’.
In the Greek health care center telepsychiatry is used for psychiatry in remote places. Below are two articles about telepsychiatry in Greece.
Presented by: Northeast Telehealth Resource Center Presenters: Don Hilty, MD, USC Keck School of Medicine and Kaweah Delta Medical Center Terry Rabinowitz, MD, DDS, University of Vermont College of Medicine and University of Vermont Medical Center Telepsychiatry is a well-established, evidence-based tool to increase access to quality mental health services. Two leaders in the field will explore effective telepsychiatry models, from traditional clinical settings to integration into rural primary care, nursing homes, and beyond. As reimbursement grows and regulations continue to evolve, join us to learn where to get started (or where to expand)!
-
Evaluation of the course
The purpose of this survey is to give us a better picture of your experience with E-learning. This feedback can help us to further improve E-learning. There are no 'right' or 'wrong' answers; we are interested only in your opinion. Please be assured that your responses will be treated with a high degree of confidentiality, and will not affect your assessment. Your carefully considered responses will help us improve the way this unit is presented online in the future. Thanks very much.

